
An Introduction to Digital Identity Verification
The identity verification service market was valued at $11 billion in 2022. With more companies realizing digital technology’s security and customer service advantages, forecasts predict the sector will nearly quadruple in size by 2032.
So, what’s driving this rapid growth? Why is verification so important in the first place? And, most importantly, how can your financial institution, government agency, or organization benefit from a digital solution?
Don’t go searching for answers — you are in the right place. Here, we’ll address verification from top to bottom. Read on to learn the ins and outs of digital identity verification and why it’s essential for your business.
What is identity verification?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines identity verification as the process of confirming or denying that a claimed identity is correct. In other words, it’s how you determine whether or not someone is who they say they are.
This process normally involves comparing the requesting individual against one or more trusted identity documents. Identity verification is especially important for businesses during the account creation process, whether that be for government, financial institutions or enterprises.
Why? Because, without proper identity verification, fraudsters may be given access to services fraudulently. Bad actors often attempt to use someone else’s personal information to commit identity theft. In turn, the identity verification process is essential to preventing fraud — especially online.
What’s the difference between traditional and digital identity verification?
ID verification has been a paper-based process for many years. This required all identity proofing steps to be performed in person, involving paper forms, manual checks, and other error-prone, time-consuming processes.
Not only is this time-consuming and labor-intensive , but it also makes for a burdensome customer experience — and with that, there are lasting consequences.
Fortunately, recent years have witnessed a marked improvement in biometric technologies, paving the way for digital identity verification.
In simple terms, digital identity verification is the process of proving an identity is real without necessarily interacting in person. Rather than making manual, in-person checks, organizations can now collect biographic and biometric data digitally, at a distance, and match it against trusted sources.
A digital identity might be defined as the total sum of a person’s online presence — an electronic representation that’s used to access online services, make purchases, and interact with others. It can be made up of many components, such as:
- A government-issued identity document, such as a driver’s license or state ID
- Digital identity documents, like eIDs and ePassports
- Mobile data
- Phone numbers and email addresses
- Transaction histories
- Biometric data
- Social media information
Generally speaking, online identity verification is an umbrella term for the process of checking that submitted information — such as the types listed above — is valid and genuinely belongs to the person submitting it. If it isn’t, there’s a chance the individual in question isn’t who they claim to be.
Why is digital identity verification important?
Identity verification methods are top of mind for organizations around the world. Why? Three key variables are in play, fueling the push toward digital verification at an increasingly rapid pace.
1. Global growth in trade and travel
The race to digitize interactions has led to great innovation and economic growth. On the flip side, it has also provided ample opportunities for fraud. Companies are looking to implement various security measures to protect their interaction with customers. Simultaneously, as governments around the world move toward digitized citizen services, the verification process is a critical piece of the puzzle.
In realization of this fact, governments are increasingly funding and supporting digital ID authentication technologies. Take the United States, for example. In September 2022, the Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Government Affairs proposed the Improving Digital Identity Act. The legislation would establish a task force to coordinate federal, state, and private-sector efforts to develop digital identity credentials, such as driver’s licenses, passports, and birth certificates.
Globally, nearly 160 out of 200 countries are already issuing ePassports, a machine-readable document with an embedded chip. With 1.2B ePassports now in circulation and a strong push behind biometrics (particularly facial recognition), authorities are offering travelers a taste of cross-border movement that is as secure as it is swift and seamless.
2. Customer experience and preferences
Today’s consumers are used to having everything at their fingertips, accessible with just the click of a button. Comparatively, outdated or manual processes are both frustrating and time-consuming. In fact, 90% of businesses have lost potential customers during the initial onboarding process.
With digital ID verification a central component of onboarding, it’s essential for organizations to implement a fast and frictionless solution. As identity verification methods mature, many are looking for new, more advanced, and seamless processes that maximize security without compromising user experience.
3. Identity theft and fraud
Although financial crime has always been an incessant threat, the rise of digital payment services has made way for a new era of identity fraud. Online transactions involve sensitive financial and personal data, making them a lucrative target for bad actors hoping to score an easy payday.
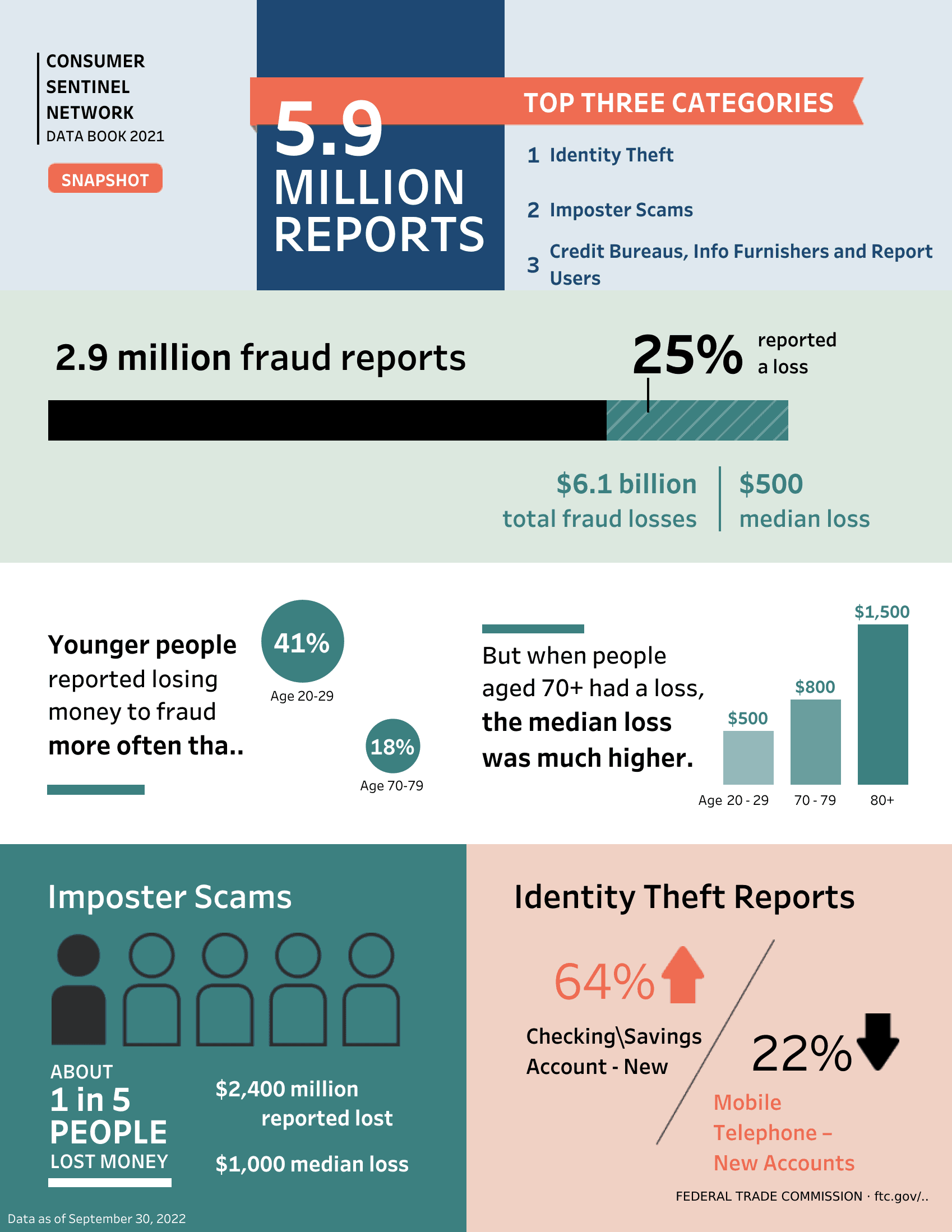
According to the U.S. Federal Trade Commission, 2.9M fraud reports were filed as of 2022 and identity theft was the top category for consumer complaints. 25% of these cases reported a loss, resulting in over $6.1 billion lost to identity fraud.
Clearly, there’s ample evidence that the world is in dire need of digital verification. With financial services increasingly under fire from fraudsters, securing personal information has never been more important.
What are the benefits of digital ID verification?
On the bright side, financial institutions can level the playing field by deploying best-in-class authentication tools. Plus, with the right identity verification solution at their side, they can unlock an array of notable business advantages:
- Operational efficiency: The digital verification process is much faster and less burdensome than traditional methods. With more time and resources to spare, you can streamline authentication and dedicate labor to other critical tasks.
- Compliance: Financial services providers have strict legal obligations when it comes to protecting personal information, combating fraud, and verifying identity data. Digital ID proofing will help satisfy compliance requirements while providing a high degree of assurance.
- Customer acquisition: Online identity verification removes a tedious barrier of entry for consumers hoping to open accounts and complete transactions without jumping through hoops.
- Risk management: With additional authentication methods like liveness detection and facial recognition, you can support a layered security strategy that mitigates risk.
How does digital identity verification work?
Before you implement an identity verification solution, it helps to understand how it works in practice. Although multiple approaches are available, they are all based on a central premise: the biographic data about a person needs to be tied securely to the human who is applying for a service, making a purchase or opening an account. This is achieved by using biometric data (a facial image or fingerprint, for example) as the secure link between the person and the data.
There are several commonly-used elements in digital identity programs:
- Knowledge-based verification: This involves requesting identity data only the real person should know — a password, physical address, their mother’s maiden name, etc.
- Document verification: This technique requires a government-issued identity document, like a passport or driver’s license. The physical ID document is checked by a machine to confirm its validity.
- Biometric verification: This method uses biometric data to confirm an individual’s identity. This may involve the use of fingerprint, iris, or facial recognition software.
- Device authentication: Some devices may be trusted, whereas others could be dangerous. This method verifies the device’s reputation, usually by confirming its IP address or browser fingerprint.
- One-time password: A unique, one-use only code is sent to the user via email or text, to ensure they are in control of the device.
Verify identities with Entrust
Entrust offers a robust identity verification (IDV) solution that validates the user you’re interacting with as a real person linked to the genuine ID document that proves their digital identity. Entrust IDV offers remote, scalable verification services at the highest level of identity assurance for crucial government-to-citizen programs.
With the choice of best-of-breed technologies, IDV has the flexibility and secure processes to meet each government’s policy, technical, and budget requirements. Our innovative solution utilizes smartphone reading and validation of electronic machine-readable travel documents (eMRTDs) — ePassports or eIDs — combined with compliant and quality biometrics matched to the individual.
How close are you to achieving a robust identity verification solution that caters to your business needs? No matter the distance, we can help you get there. Learn more about how Entrust enables identity verification for your government-to-citizen interactions today.
