What Is Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an authentication method that requires a user to provide at least two factors of verification in order to be granted access to a website, application or resource.
What is the importance of MFA?
MFA enhances an organization's security by requiring additional factors to verify a user. As usernames and passwords have proven to be vulnerable to attack, organizations wishing to enhance their security can turn to MFA to ensure a higher degree of confidence and potential to allow verified users access to websites, applications, and resources.
How does MFA work?
MFA requires a user to provide at least one additional factor of verification to be granted access. Enforcing a factor beyond the user name and password ensures a higher level of security by asking for additional information that is easy for authentic users to provide, and very hard for cybercriminals to have at their disposal.
In general, the process is:
- A user enters a username and password to access an account.
- A second factor of verification is requested, such as a fingerprint, PIN, or One-Time Password (OTP).
- The user provides the factor requested, which is based on information previously provided by them when they set up their account.
Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) a form of MFA?
Yes, it is. 2FA is one form of MFA, in which a user is required to provide exactly two factors of verification.
What are the four types of factors?
There are four types of factors that can be provided to verify a user:
- Knowledge: something the user knows.
- Possession: something the user has.
- Biometric: something the user is.
- Location: somewhere the user is.
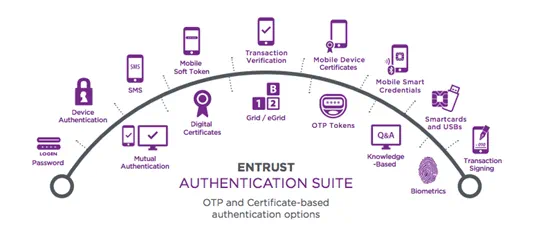
What are the most common authenticators/authentication tokens?
Transparent Authentication
Transparent authenticators that validate users without requiring day-to-day involvement.
- Digital Certificates
- IP-Geolocation
- Device Authentication
Physical Form Factor Authentication
Tangible devices that users carry and use when authenticating.
- One-Time Passcode (OTP) Tokens
- Display Card
- Grid Authentication
- One-Time Passcode List
- Biometrics
Non-physical Form Factor Authentication
Methods of verifying user identities without requiring them to carry an additional physical device.
- Knowledge-Based Authentication
- Out-of-Band Authentication
- Mobile Smart Credentials
- SMS Soft Tokens
What is adaptive authentication (risk-based authentication)?
Adaptive authentication, also known as risk-based authentication, analyzes the risk of the user profile against the access being requested. The higher the risk of a user profile, the stronger the challenges will be. With adaptive authentication, you can challenge the user for additional factors or credentials when the risk level is appropriate.
Organizations can determine their own risk levels, but in general, the riskiness of a user profile is based on policies around where users are logging in from, when they are logging in, the device they are using to log in, and if they are connecting via a public or private network.
Which Entrust solutions support MFA?
Entrust supports a wide range of identity and access management (IAM) solutions, including MFA.