Decentralized Identity
Put your users in control of their identity while enhancing their user experience with seamless access to applications and services.
What is decentralized identity (DeID)?
Decentralized identity (DeID) gives individuals full ownership and control of their identities and its associated attributes. All the information used to build an identity is encrypted, signed, and protected with digital keys that can be used to confirm an individual’s identity without ever exposing the sensitive information aspects of that identity. Relying parties (Employers, governments, and retailers) don’t store critical and sensitive user identity attributes. Users store all encrypted identity related information in a digital wallet on hardware protected area on their mobile device.
Why do you need DeID?
Improve Privacy
Allow individual users to own their digital identity with a greater focus on privacy, control, security, and ease of use.
Enforce Compliance
Organizations can issue and verify identities without having to request access to or store a user’s private data, thereby improving compliance and reducing potential credential theft and fraud.
Simplify Development
Developers can build applications and services that without the need to store user credentials or sensitive personal identifying information (PII).
How does DeID work?
With DeID, when interacting with a service provider (a relying party like an employer, government, or retailer), a user only needs to share the required information without providing full access to their complete identity document. For example, if a user needs to prove they are over 18 years of age, they can do so without providing access to their driver’s license number or date of birth. The user can simply provide a zero knowledge proof of over 18 years of age, which is a predicate/attestation like “born after a specific date."
A typical DeID journey
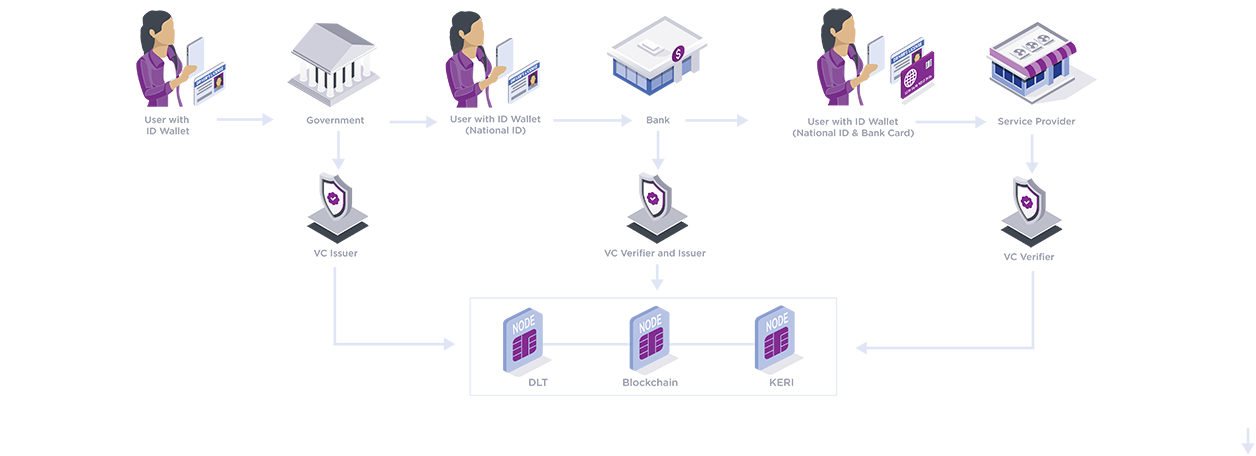
- A user with a digital wallet app, may verify their identity with a government entity with an ID verification service using existing identity documents such as passports, driver licenses, etc. Once the identity is verified, a verifiable credential (VC) is then issued to the user by the Identity as a Service platform. The individual VC is stored in the user’s digital wallet.
- Using the initial National ID based VC, a bank or other entity can issue banking / other credentials to the user in the form of VCs that is also stored in the digital wallet of the user.
- When a user interacts with a service provider (eg. an e-commerce vendor), they can provide their VC from their digital wallet which the service provider can verify via the Identity as a service platform that can facilitate the verification without having to interact with the issuer.
What the experts are saying...

Schedule a consultation with our decentralized identity center of excellence team to learn how you can prepare and get started on your decentralized identity journey.